In a Goal/Objective Matrix, the established goals are related to the intended objectives. Like all matrices, it shows the relationship between two elements. Furthermore, by creating this cross-mapping, it becomes clear which objectives contribute to the achievement of which goals.
Objectives, like goals, align with the organization’s strategy. Also like goals, they are defined in a specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound manner. Objectives serve as actionable guidelines that guide architectural decisions, resource allocation, and performance measurement. Concurrently, objectives provide a more concrete and detailed expression of the broader goals, breaking them down into manageable and achievable components. Thus, they serve as actionable targets that guide the organization’s efforts in pursuit of its strategic intent.
Definition
Setting goals and defining objectives are the most difficult parts of formulating a strategy. The objectives must demonstrate that the implementation of the strategic plan is likely to achieve the intended overarching goals.
An objective is a quantitative, actionable and measurable result that defines strategy and achieves a goal1.
In practice, however, the formulated objectives are often too focused on concrete actions to be taken. This is because senior management often thinks from an overly operational perspective. As a result, this common situation means that in most cases what the company wants to achieve is lost. The consequences of formulating activities versus a goal-oriented strategic planning approach often result in unclear measures of success. This leads to an inability to determine whether an objective has been achieved and whether an initiative has failed or succeeded. The SMART method described when creating the Strategy/Goal Matrix can help to formulate objectives correctly.
Gathering information
Asking senior management the following questions will help to get a clear picture of the objectives that need to be defined to achieve the organization’s goals:
- What exactly must the organization do to achieve its goals?
- What happens if the organization doesn’t?
- What (actionable) steps need to be taken?
- Can the steps be clearly defined and made SMART?
- How can progress toward the objective be made measurable?
When objectives are not linked to clear business goals, unanticipated challenges often arise. This happens in areas that are seemingly unrelated to the objective in question. And in nine out of ten cases, it comes to light only later. As a result, the problems are less easily traced back to the objectives that were set incorrectly (too activity-oriented) at an earlier stage.
Creating the matrix
In a Goal/Objective Matrix, the established goals are related to the intended objectives. Like all matrices, it shows the relationship between two elements. By creating this cross-mapping, it becomes clear which objectives contribute to the achievement of which goals.
- Record all the goals and objectives deduced from the organization’s strategy.
- Compare the objectives and make sure they are all sufficiently different from one another.
- Link the objectives to the various goals.
- Take extra care to link the objectives to all possible goals they have a relation with.
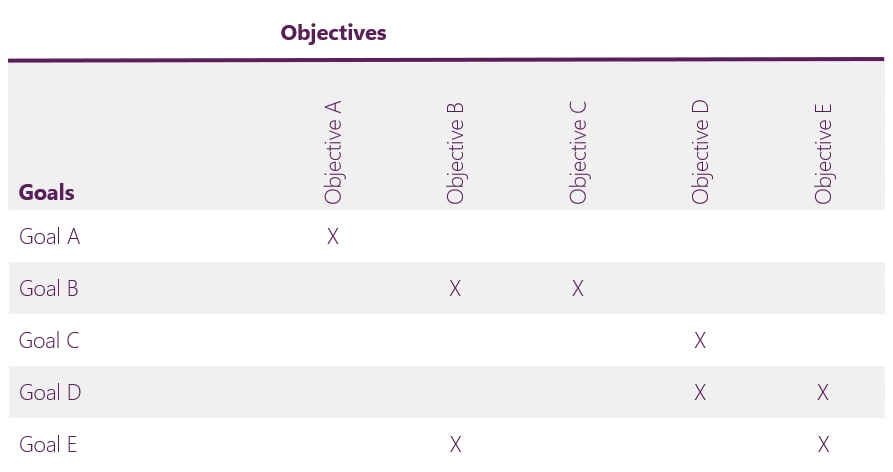
Objectives should be specific, quantifiable and achievable targets that need to be met in order to achieve the associated goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) and related metrics provide the means to determine whether or not an objective has been met.
More information
For additional information about creating a Goal/Objective Matrix, please refer to Chapter 8, Section 8.3.3.3, of my book Getting Started with Enterprise Architecture.
Back to
- Business Architecture Guild®, A Guide to the Business Architecture Body of Knowledge®, vol. 11.0. 2022. ↩︎
